1. Understanding the Zig Zag Indicator
When configuring the Zig Zag Indicator, traders must be mindful of the trade-off between sensitivity and the relevance of the data. A high sensitivity setting will result in more frequent zigzags, potentially capturing more short-term trends but also increasing the risk of noise. Conversely, a lower sensitivity setting will produce fewer, more significant trend lines, which may be more useful for long-term analysis but could miss shorter-term opportunities.
The application of the Zig Zag Indicator extends to various trading strategies:
- Swing Trading: By highlighting significant highs and lows, the Zig Zag Indicator is an asset for swing traders looking to capture gains in a market within an uptrend or downtrend.
- Channel Trading: Traders can use the indicator to draw trend channels, which can help in determining optimal entry and exit points.
- Elliott Wave Theory: The Zig Zag Indicator can assist in identifying the wave patterns that form the basis of this complex technical analysis strategy.
Integration with other technical tools can enhance the effectiveness of the Zig Zag Indicator. For instance, combining it with Fibonacci retracement levels can provide additional validation for potential support and resistance zones. Similarly, using the indicator in conjunction with moving averages or oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can offer a more comprehensive analysis of market momentum and potential trend reversals.
Practical considerations for traders include:
- Market Conditions: The indicator is most effective in markets with clear trends and may be less useful in ranging or sideways markets.
- Asset Volatility: Volatile assets might require adjustments to the Zig Zag parameters to filter out excessive noise.
- Historical Testing: Before applying the indicator to live trading, backtesting strategies using historical data can help in understanding its behavior and optimizing settings.
Incorporating the Zig Zag Indicator into a trading arsenal requires a balance between technical precision and a clear understanding of market dynamics. By doing so, traders can leverage this tool to discern meaningful price movements and make more informed trading decisions.
1.1. What is the Zig Zag Indicator?
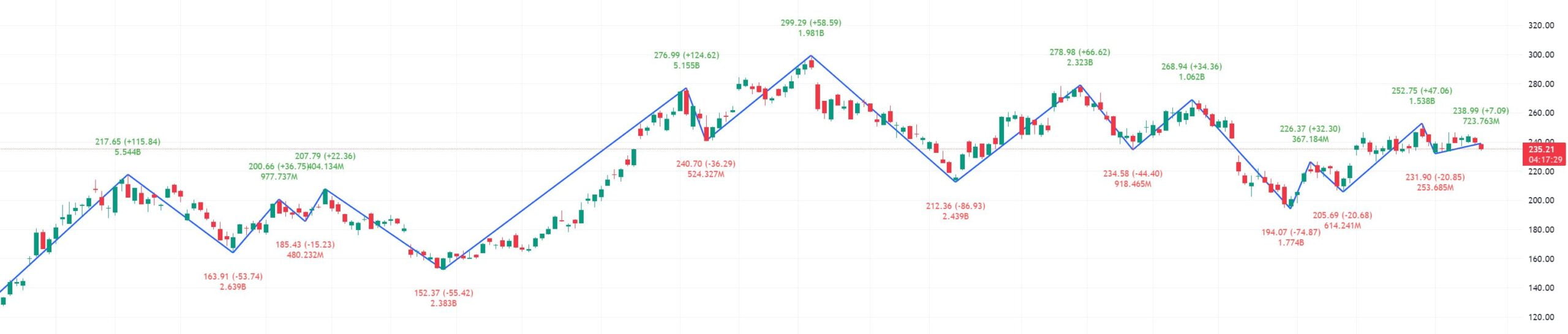
The Zig Zag indicator is a versatile tool that serves to streamline the analysis of market price movements. By eliminating the insignificant fluctuations in price, the indicator assists traders in focusing on the substantial trends that matter. Here’s how the Zig Zag indicator can be utilized effectively:
- Filtering the Noise: By setting a specific percentage, the indicator filters out the minor price changes that can distract from the overall trend.
- Chart Clarity: The resulting lines provide a clearer picture of the market, making it easier to interpret price action.
Practical Applications for Traders
Traders leverage the Zig Zag indicator for various practical applications:
- Support and Resistance: The peaks and troughs identified by the Zig Zag lines often align with support and resistance levels, which are pivotal for entry and exit points.
- Pattern Recognition: Recognizing patterns like head and shoulders or double tops and bottoms becomes more straightforward, aiding in predictive analysis.
- Fibonacci Retracements: The indicator can help in spotting ideal points for drawing Fibonacci retracements, a common technique for identifying potential reversal levels.
Complementary Analysis Tools
While the Zig Zag indicator is powerful, it should not be the sole tool for decision-making:
- Combining Indicators: Use in conjunction with other indicators like moving averages, RSI, or MACD to validate the signals provided by the Zig Zag indicator.
- Fundamental Analysis: Incorporate fundamental analysis to understand the broader market conditions that could affect the validity of the technical signals.
Key Considerations for the Zig Zag Indicator
| Aspect | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Retrospective Nature | Understand that the indicator is backward-looking and adjusts as new data comes in. |
| Real-time Reliability | Be cautious as the indicator can redraw itself, which may affect real-time decision-making. |
| Percentage Setting | Choose an appropriate percentage filter based on the volatility and time frame of the market being analyzed. |
By integrating the Zig Zag indicator into a comprehensive trading strategy and using it to enhance the analysis of market trends and patterns, traders can better navigate the complexities of the financial markets. Always remember to back-test any strategy incorporating the Zig Zag indicator to ensure its effectiveness in live trading scenarios.
1.2. The Role of the Zig Zag Indicator in Trend Analysis
The Zig Zag indicator is a dynamic tool for traders who aim to enhance their technical analysis. It operates by eliminating price noise, which is especially useful in volatile markets where price fluctuations can lead to confusion and misinterpretation of market trends.
Key Functions of the Zig Zag Indicator
- Trend Confirmation: By connecting significant highs and lows, the Zig Zag indicator provides a clearer picture of the market trend.
- Pattern Recognition: It helps in identifying classic chart patterns, making it easier for traders to execute strategies based on these formations.
- Support and Resistance: The indicator highlights key reversal points, aiding in the determination of support and resistance levels.
Practical Applications for Traders
- Chart Clarity: The Zig Zag indicator filters out minor price movements, allowing traders to focus on the significant trends.
- Strategic Planning: It can be used to draw trend lines and plan trades around support and resistance levels.
- Fibonacci Retracements: The indicator’s ability to identify significant price points makes it an excellent tool for applying Fibonacci retracement strategies.
Integration with Other Tools
- Confirmation Tool: The Zig Zag indicator can be used alongside other technical analysis tools, such as moving averages or oscillators, to confirm trend directions or potential reversals.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Traders can apply the Zig Zag indicator across different timeframes to gain insights into both short-term and long-term trends.
By focusing on significant price movements, the Zig Zag indicator serves as a lens through which traders can view the market, stripping away the unnecessary to reveal the essential patterns and trends that drive their trading decisions. Whether as a standalone tool or in conjunction with other indicators, it remains a staple in the trader’s toolkit for its simplicity and effectiveness in trend analysis.
1.3. Key Components of the Zig Zag Indicator
The Zig Zag Indicator serves as a strategic asset for traders aiming to cut through market noise and spot significant trends. Its effectiveness hinges on the proper adjustment of its integral settings: Depth, Deviation, and Backstep.
| Component | Function | Impact on Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Determines the minimum number of bars without a new high or low | Higher values filter minor movements, revealing major trends |
| Deviation | Sets the required price movement percentage for directional changes | Higher values reduce sensitivity, lower values may increase market noise |
| Backstep | Defines the minimum bar interval for plotting highs and lows | Ensures accurate historical representation and prevents repainting |
Traders should note that a balance is essential when configuring these settings. An overly high Depth or Deviation might cause the trader to miss out on profitable short-term opportunities, while too low of a setting could result in a flood of insignificant trend lines. Similarly, an appropriate Backstep value is crucial to avoid false signals that could mislead trading decisions.
Effective use of the Zig Zag Indicator can help traders to identify pivotal points in the market, support resistance levels, and classic chart patterns such as head and shoulders or triangles. By doing so, traders can make more informed decisions, whether they’re looking to enter or exit positions or place stops and limits.
Practical application involves backtesting the indicator with historical data to fine-tune the settings for a specific market or asset. Traders might also combine the Zig Zag Indicator with other analytical tools like moving averages, Fibonacci retracement levels, or momentum oscillators for a more robust trading strategy.
Incorporating the Zig Zag Indicator into a trading arsenal requires a blend of technical acumen and strategic foresight. Mastery of its settings can provide traders with a clearer view of the market’s direction, aiding in the pursuit of profitable trades.
2. Optimizing Zig Zag Settings for Enhanced Trading Performance
Adjusting the Zig Zag indicator settings is a strategic approach to align the tool with one’s trading style and objectives. Traders should consider their time frame and volatility of the market when configuring the indicator.
| Zig Zag Parameter | Short-Term Trading | Long-Term Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Lower (e.g., 5-10) | Higher (e.g., 12-20) |
| Deviation | Lower (e.g., 1-3%) | Higher (e.g., 5-10%) |
| Backstep | Lower (e.g., 1-3) | Higher (e.g., 3-5) |
Depth adjustment is directly related to the frequency of trades. Day traders might prefer a lower depth to capitalize on small price movements, while swing traders might increase the depth to highlight only significant trends.
The deviation setting is tied to the market’s volatility. In a highly volatile market, a larger deviation can help filter out noise, whereas in a less volatile market, a smaller deviation might be sufficient to capture meaningful movements.
Backstep value is crucial for the integrity of the chart patterns. Traders must ensure that the Zig Zag does not adjust its lines retrospectively too often, as it can create confusion and lead to inaccurate analysis.
By combining indicators, traders can gain multiple perspectives on the market. For instance:
- Zig Zag and Moving Averages: Helps in confirming trend direction when the Zig Zag lines align with moving average crossovers.
- Zig Zag and RSI (Relative Strength Index): Can signal overbought or oversold conditions when there’s a divergence between the Zig Zag patterns and the RSI readings.
- Zig Zag and Fibonacci Retracements: Useful for identifying potential support and resistance levels during retracements in a trend.
When integrating the Zig Zag with other indicators, it’s crucial to ensure that each indicator serves a distinct purpose and provides unique insights, rather than overlapping information. Diversification of analysis techniques can lead to a more balanced and informed trading strategy, reducing the risk of misinterpretation and enhancing the potential for profitable trades.
2.1. Adjusting the Depth: Finding the Sweet Spot
When configuring the Zig Zag indicator, the depth setting plays a pivotal role. It acts as a filter, defining the minimum price movement considered significant enough to draw a new line. By adjusting the depth, traders can tailor the indicator to highlight larger trends and ignore minor fluctuations, which could be mere market noise.
The ideal depth setting can vary depending on the market and the asset being traded. A typical starting point for the depth is within the 5% to 10% range. This is a balanced approach, avoiding an overly sensitive setting that captures every minor price change, and a setting that’s too insensitive, potentially missing out on significant trends.
| Market Condition | Suggested Depth Setting |
|---|---|
| High Volatility | Higher Depth (>10%) |
| Low Volatility | Lower Depth (<5%) |
Traders should consider the asset’s volatility when selecting the depth setting. For highly volatile assets, a greater depth helps to filter out the frequent but insignificant price movements. Conversely, in markets with lower volatility, a smaller depth could be more appropriate to ensure that smaller yet relevant trends are not overlooked.
Backtesting is a crucial step in optimizing the depth setting of the Zig Zag indicator. By applying different settings to historical data, traders can observe the impact on past performance and refine their settings accordingly. This process helps in creating a customized approach that aligns with individual trading strategies and market conditions.
Experimentation with depth settings in a risk-free environment, such as a demo account, is essential. It allows traders to observe the impact of different settings in a live market scenario without the risk of losing capital. Through trial and error, traders can identify the depth setting that best suits their trading style and the specific characteristics of the market they are trading in.
In practice, adjusting the Zig Zag indicator’s depth setting is a dynamic process, requiring ongoing assessment and refinement as market conditions change. Traders must remain vigilant and ready to adapt their settings to maintain the effectiveness of their trading strategies.
2.2. Deviation Settings: Balancing Sensitivity and Noise
When configuring the Zig Zag indicator, understanding the impact of deviation settings on the chart is paramount. The deviation is the minimum price move required to continue the Zig Zag line; if the price moves less than the deviation percentage, the indicator remains unchanged. This mechanism is what allows the Zig Zag to eliminate insignificant price movements and bring clarity to the market’s underlying direction.
Deviation Settings Impact:
| Deviation Setting (%) | Sensitivity | Noise Reduction | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher (>10%) | Low | High | High Volatility Instruments |
| Moderate (5-10%) | Medium | Medium | Average Volatility Instruments |
| Lower (<5%) | High | Low | Low Volatility Instruments |
Customization is key when utilizing the Zig Zag indicator. Traders should not rely on default settings but rather adjust the deviation according to the specifics of the trading instrument and market conditions. For instance, in a fast-moving market, a higher deviation might be necessary to avoid misleading signals due to high volatility.
Steps for Adjusting Deviation:
- Identify the Volatility: Assess the historical volatility of the asset to determine a starting point for the deviation setting.
- Set Initial Deviation: Apply the Zig Zag indicator with the chosen deviation percentage.
- Analyze Chart Patterns: Observe the resulting chart for clarity of trend lines and frequency of reversals.
- Backtest for Optimization: Conduct backtesting with different settings to measure the effectiveness of the Zig Zag pattern in capturing significant moves.
- Adjust Accordingly: Fine-tune the deviation setting based on backtesting results and real-time observation to achieve the best balance between sensitivity and noise reduction.
By carefully adjusting the deviation settings, traders can enhance their technical analysis and improve the accuracy of their trend-following strategies. It’s important to remember that no single setting will work in all market conditions; flexibility and ongoing adjustment are critical components of effectively using the Zig Zag indicator.
2.3. Backstep Value: Ensuring Clarity in Chart Patterns
When utilizing the Zig Zag indicator, understanding and adjusting the backstep value is crucial for accurate market analysis. The backstep value impacts the sensitivity of the indicator to the market’s price movements. It’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all setting; rather, the optimal value is influenced by market conditions and trading strategy.
Adjusting the Backstep Value: Key Considerations
- Market Volatility: In highly volatile markets, a higher backstep value might be necessary to filter out noise and focus on more substantial price moves.
- Trading Horizon: Short-term traders may need a lower backstep to respond to quick market changes, while long-term traders can use a higher value to identify larger trends.
- Chart Clarity: The chosen backstep value should make the chart patterns clearer and more interpretable for the trader.
- Indicator Responsiveness: A lower backstep value increases the indicator’s responsiveness, which can be both an advantage for capturing quick moves and a disadvantage due to potential false signals.
Common Backstep Values and Their Implications
| Backstep Value | Implication for Traders |
|---|---|
| 1 | Highly sensitive, may lead to overreacting to minor price changes |
| 2-3 | Balanced sensitivity, suitable for moderate market conditions |
| 4-5 | Less sensitive, better for highlighting significant trends |
Continuous Adjustment and Backtesting
Traders should not remain static with their backstep value settings. Continuous adjustment is key to adapting to changing market dynamics. It’s advisable to backtest different backstep values against historical data to gauge their effectiveness in identifying profitable trading opportunities.
Practical Application
To apply the backstep value effectively, traders should:
- Start with a default value and observe the indicator’s performance.
- Adjust the value incrementally, noting the changes in the indicator’s behavior.
- Backtest the setting against historical data to validate its effectiveness.
- Apply the optimized backstep value in live trading, but remain open to making further adjustments as needed.
By carefully managing the backstep value, traders can enhance their use of the Zig Zag indicator, making it a more powerful tool for identifying market trends and making informed trading decisions.
2.4. Combining Zig Zag with Other Technical Indicators
Incorporating the Zig Zag indicator with other technical analysis tools can significantly enhance a trader’s market insight. Here’s a breakdown of how to effectively combine the Zig Zag with various indicators:
Zig Zag and Moving Averages
- Signal Confirmation: A Zig Zag line crossing a moving average may indicate a potential trend reversal.
- Period Selection: Align the moving average period with the Zig Zag settings for consistency.
- Trend Analysis: Use multiple moving averages with different periods to gauge short-term and long-term trends.
Zig Zag and MACD
- Divergence Spotting: Look for differences between Zig Zag peaks/troughs and MACD lines to identify potential reversals.
- Momentum Confirmation: MACD crossovers in conjunction with Zig Zag pivot points can confirm momentum shifts.
- Confluence: MACD histogram and Zig Zag indicator agreement can add weight to buy or sell signals.
Zig Zag and RSI
- Strength Validation: An RSI reading that matches a Zig Zag pivot point can confirm the validity of support or resistance levels.
- Overbought/Oversold Conditions: RSI levels above 70 or below 30 can indicate potential reversals that align with Zig Zag pivot points.
- Divergence Analysis: Similar to MACD, RSI divergence from Zig Zag patterns can signal impending trend changes.
Zig Zag and Fibonacci Retracement
- Price Reaction Levels: Zig Zag swings that align with Fibonacci levels may suggest strong reaction points in the market.
- Entry/Exit Points: Use Fibonacci retracement in conjunction with Zig Zag to identify strategic trading opportunities.
- Confluence Zones: Multiple Fibonacci levels converging with Zig Zag lines increase the probability of a significant price level.
Best Practices for Combining Indicators with Zig Zag
- Validation: Use additional indicators to validate Zig Zag signals, not as standalone confirmation.
- Contextual Analysis: Always consider the broader market context when interpreting signals from technical indicators.
- Customization: Adjust indicator settings to fit personal trading styles and the specific asset being traded.
- Risk Management: Combine technical analysis with sound risk management strategies to protect against false signals.
By strategically combining the Zig Zag indicator with other technical analysis tools, traders can create a multi-faceted approach to market analysis, leading to more informed trading decisions and the potential for increased profitability.
3. Practical Tips for Applying Zig Zag Indicator Settings

Adapting Zig Zag Settings for Market Volatility
- Volatile Markets:
- Increase the deviation setting to reduce noise and focus on significant trends.
- Filter out minor price changes that are irrelevant to the broader market direction.
- Less Volatile Markets:
- Decrease the deviation setting to capture smaller price movements.
- Identify subtle trends that could lead to profitable trading opportunities.
Zig Zag Indicator and Risk Management
- Stop Loss Settings:
- Place stop losses below swing lows in uptrends for protection against reversals.
- Adjust stop loss positions in response to new peaks and troughs identified by Zig Zag.
- Take Profit Settings:
- Set take profits near recent highs where price may encounter resistance.
- Use Zig Zag peaks as benchmarks for potential exit points to lock in profits.
Time Frame Considerations
- Day Trading:
- Use a shorter time frame and a more sensitive Zig Zag setting.
- Capture quick price movements that occur within the day.
- Long-Term Trading:
- Opt for a longer time frame and a less sensitive Zig Zag setting.
- Gain insight into the long-term trend and overall market direction.
Zig Zag Settings Across Different Markets
- Forex Market:
- May require specific settings due to the 24-hour trading cycle and liquidity.
- Stock Market:
- Adjust settings to account for market open/close and individual stock volatility.
- Commodities Market:
- Tailor Zig Zag settings to the unique trends and cycles in commodities trading.
Combining Zig Zag with Other Technical Indicators
- Moving Averages:
- Confirm Zig Zag signals with moving average crossovers or supports/resistances.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence):
- Use MACD to validate Zig Zag trend reversals and momentum shifts.
- Multi-Indicator Strategy:
- Enhance the reliability of Zig Zag signals by corroborating with other indicators.
- Test different combinations to find the most effective multi-indicator approach.
3.1. Case Scenarios: When to Tweak Zig Zag Settings
Adjusting Zig Zag Indicator Settings for Market Conditions
Traders must be vigilant in modifying the settings of the Zig Zag indicator to suit the prevailing market conditions. Here’s how different settings can be optimized:
In Volatile Markets:
- Depth Setting: Increase this to filter minor price changes and highlight significant trends.
- Deviation Setting: If the indicator repaints frequently, increase this to decrease sensitivity.
- Backstep Value: Adjust this to ensure the indicator captures the actual market peaks and troughs.
In Low Volatility or Short-Term Trading:
- Depth Setting: Decrease to identify relevant short-term trends.
- Deviation Setting: Reduce to make the indicator more responsive to recent price movements.
- Backstep Value: Lower the value to include short-term reversals in the analysis.
Adjustment Guidelines:
| Market Condition | Suggested Adjustment | Zig Zag Setting |
|---|---|---|
| High Volatility | Increase | Depth |
| High Volatility | Increase | Deviation |
| Low Volatility | Decrease | Depth |
| Rapid Market Shift | Decrease | Deviation |
| Omitting Reversals | Decrease | Backstep |
Continuous Evaluation:
- Traders should regularly assess the Zig Zag’s performance.
- Adaptability is key; settings should be adjusted as market dynamics change.
- By fine-tuning the Zig Zag, traders ensure it remains a valuable tool for technical analysis.
By tailoring the Zig Zag settings to the specific characteristics of the market environment, traders can enhance their analytical precision and potentially improve their trading outcomes.
3.2. Risk Management: Using Zig Zag to Set Stop Loss and Take Profit
Incorporating the Zig Zag indicator into a trading strategy requires an understanding of its settings, which typically include the percentage change parameter. This setting determines the minimum price movement required for the Zig Zag to draw a new line. A higher percentage will filter out smaller price movements, resulting in fewer, more significant lines that can help identify major support and resistance areas.
Optimization of Zig Zag Settings:
| Percentage Change | Impact on Indicator |
|---|---|
| Lower (e.g., 5%) | More sensitive, more lines drawn |
| Higher (e.g., 15%) | Less sensitive, fewer significant lines |
By adjusting these settings, traders can tailor the indicator to their trading style and the volatility of the market they are trading. A more volatile market may require a higher percentage change to avoid too much noise, while a less volatile market might be better served with a lower percentage to capture more subtle moves.
Combining Zig Zag with Other Indicators:
- Fibonacci Retracement: Align Zig Zag peaks and troughs with Fibonacci levels to identify potential reversal points.
- Moving Averages: Use moving averages to determine the overall trend direction and filter Zig Zag signals accordingly.
- Volume Indicators: Confirm Zig Zag signals with volume increases, suggesting stronger market commitment to the price change.
Traders must also be mindful of the psychological aspects of trading when using the Zig Zag indicator. Setting stop loss and take profit orders can be emotionally challenging, as it involves accepting potential losses and gains. The clarity provided by the Zig Zag can help in making these decisions more systematic and less influenced by emotional bias.
Effective Risk Management with Zig Zag:
- Identify significant price reversals using the Zig Zag lines.
- Set stop loss orders just beyond the latest Zig Zag reversal point.
- Determine take profit levels by projecting potential future Zig Zag points.
- Adjust orders as new Zig Zag points are formed to maintain risk parameters.
- Combine with other indicators to validate and strengthen trading signals.
By integrating the Zig Zag indicator with a disciplined approach to risk management, traders can enhance their ability to navigate the markets with greater confidence and precision.
3.3. Time Frames: Adapting Zig Zag Settings for Different Markets
Adapting Zig Zag Settings to Different Time Frames
| Time Frame | Typical Markets | Recommended Zig Zag Settings | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short (1-15 min) | Forex, Cryptocurrencies | Lower depth | To capture short-term trends and provide quick trade signals |
| Long (Daily, Weekly) | Equities | Higher depth | To filter out minor price changes and highlight long-term trends |
Importance of Deviation Percentages
- Lower Time Frames: A smaller deviation can result in excessive signals, increasing the risk of false positives.
- Higher Time Frames: A larger deviation helps eliminate market noise, making it easier to spot significant trends.
Continuous Adjustment and Backtesting
- Traders must tailor the Zig Zag settings to their specific trading strategy and the prevailing market conditions.
- Regular backtesting is essential to validate the effectiveness of the Zig Zag settings on historical data.
By understanding the relationship between time frames, market characteristics, and Zig Zag settings, traders can enhance their technical analysis and potentially improve their trading performance. It’s crucial to remember that the Zig Zag indicator is not a standalone tool but rather a complement to other technical analysis methods, which should be used in conjunction with a well-rounded trading strategy.











